版本值(Versioned Value)
用一个新的版本号来记录每次值的更新,允许读取历史值。
问题
在分布式系统中,节点需要能够知道键的哪个值是最新的。有时他们需要知道过去的值,以便能够正确地对值的变化作出反应。
解决方案
为每个值都存储一个版本值。这个版本编号在每次更新的时候自增。它允许每次更新都转换为新的写操作,而不会阻塞读操作。客户端能通过指定的版本号读取历史值。
思考一个复制键值存储的简单示例。集群 leader 处理对键值存储的所有写操作。它把所有写操作都存进 WAL 中。在主从下 WAL 是有多个的。Leader 将来自高水位标记的 WAL 日志的条目应用到键值存储中。这种标准复制方法被称为状态机复制(state-machine-replication)。大多数由共识算法(如 Raft )支持的数据系统都是这样实现的。在这种情况下,键值存储保持一个整数版本计数器。每次从预写日志应用键值写命令时,它都会增加版本计数器。然后用自增后的版本计数器构造新键。这样就不会更新现有的值,但是每个写请求都会将新值添加到后备存储(backing store)中。
class ReplicatedKVStore...
int version = 0;
MVCCStore mvccStore = new MVCCStore();
@ovveride
public CompletableFuture<Response> put(String key, String value) {
return server.propose(new SetValueCommand(key, value));
}
private Response applySetValueCommand(SetValueCommand setValueCommand) {
getLogger().info("Setting key value " + setValueCommand);
version = version + 1;
mvccStore.put(new VersionedKey(setValueCommand.getKey(), version), setValueCommand.getValue());
Response response = Response.success(version);
return response;
}
版本键的排序
因为快速导航到最佳匹配版本是一个重要的实现关注事项,所以版本控制的键的排列方式是,通过使用版本号作为键的后缀,形成自然的顺序。这维护的顺序能很好的与底层数据结构匹配。例如,如果一个键有两个版本,key1 和 key2,那么 key1 将被排序在 key2 之前。
为了存储版本化的键值,需要使用一个数据结构,例如调表,它允许快速导航到最近的匹配版本。在 Java 中,mvcc 存储可以构建如下:
class MVVCStore...
public class MVCCStore {
NavigableMap<VersionedKey, String> kv = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();
public void put(VersionedKey key, String value) {
kv.put(key, value);
}
}
通过导航哈希表来执行,VersionedKey 是通过下面这样实现的。它实现了一个比较器来让 keys 排序
class VersionedKey...
public class VersionedKey implements Comparable<VersionedKey> {
private String key;
private int version;
public VersionedKey(String key, int version) {
this.key = key;
this.version = version;
}
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public int getVersion() {
return version;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(VersionedKey other) {
int keyCompare = this.key.compareTo(other.key);
if (keyCompare != 0) {
return keyCompare;
}
return Integer.compare(this.version, other.version);
}
}
这个实现允许使用可导航的 map API 获取特定版本的值。
class MVCCStore…
public Optional<String> get(final String key, final int readAt) {
Map.Entry<VersionedKey, String> entry = kv.floorEntry(new VersionedKey(key, readAt));
return (entry == null)? Optional.empty(): Optional.of(entry.getValue());
}
思考一个示例,其中一个键有四个版本,分别存储在版本号1、2、3 和 5 中。根据客户端读取值时使用的版本,返回最匹配的键版本。
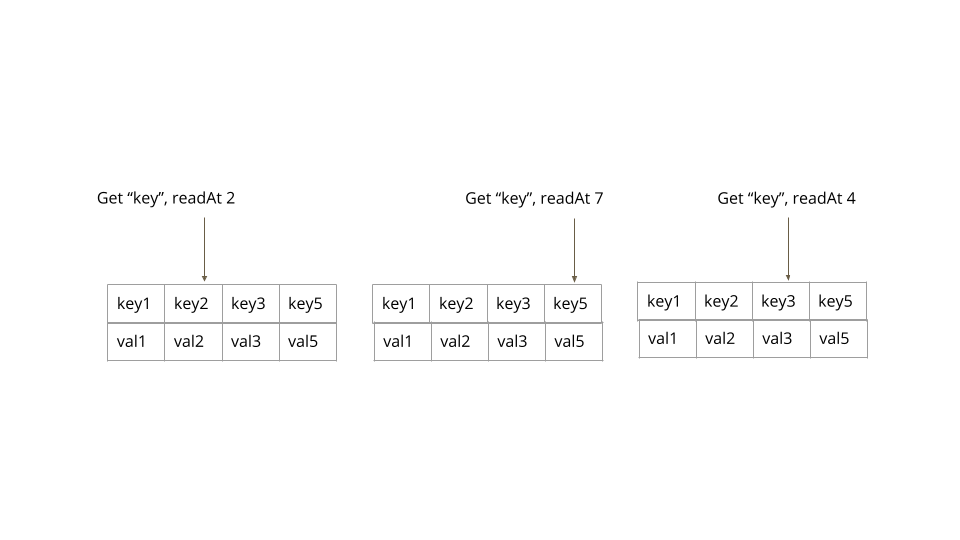
将存储特定键值的版本返回给客户端。然后客户端拿这个版本来读取值。总体工作如下。
put 请求处理
读取特定版本对应的值
多个版本读
有时客户端需要从给定的版本号获取所有版本。例如,在状态监控中,客户端需要从特定版本获取所有事件。
集群节点可以存储额外的索引结构来存储键的所有版本。
class IndexedMVCCStore…
public class IndexedMVCCStore {
NavigableMap<String, List<Integer>> keyVersionIndex = new TreeMap<>();
NavigableMap<VersionedKey, String> kv = new TreeMap<>();
ReadWriteLock rwLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
int version = 0;
public int put(String key, String value) {
rwLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
version = version + 1;
kv.put(new VersionedKey(key, version), value);
updateVersionIndex(key, version);
return version;
} finally {
rwLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
private void updateVersionIndex(String key, int newVersion) {
List<Integer> versions = getVersions(key);
versions.add(newVersion);
keyVersionIndex.put(key, versions);
}
private List<Integer> getVersions(String key) {
List<Integer> versions = keyVersionIndex.get(key);
if (versions == null) {
versions = new ArrayList<>();
keyVersionIndex.put(key, versions);
}
return versions;
}
}
然后,可以提供一个客户端 API 来读取特定版本或版本范围的值。
class IndexedMVCCStore…
public List<String> getRange(String key, final int fromRevision, int toRevision) {
rwLock.readLock().lock();
try {
List<Integer> versions = keyVersionIndex.get(key);
Integer maxRevisionForKey = versions.stream().max(Integer::compareTo).get();
Integer revisionToRead = maxRevisionForKey > toRevision ? toRevision : maxRevisionForKey;
SortedMap<VersionedKey, String> versionMap = kv.subMap(new VersionedKey(key, revisionToRead), new VersionedKey(key, toRevision));
getLogger().info("Available version keys " + versionMap + ". Reading@" + fromRevision + ":" + toRevision);
return new ArrayList<>(versionMap.values());
} finally {
rwLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
从索引更新和读取数据时,必须注意使用适当的锁定。
还有令一种替代的实现,可以用键保存所有版本化值的列表,就像在 Gossip distribution 中使用的那样,以避免不必要的状态交换。
MVCC 和事务隔离
数据库使用 Versioned Value 实现 MVCC 和事务隔离。
并发控制是关于当有多个并发请求访问相同数据时如何使用锁定。当锁用于同步访问时,所有其他请求都会被阻塞,直到持有锁的请求完成并释放锁为止。使用Versioned Value,每个写请求都会添加一条新记录(都有自己在那个时刻的数据版本)。这允许使用非阻塞数据结构来存储值。
事务隔离级别(如快照隔离)也可以自然实现。当客户端以特定版本开始读取时,即使存在多个读请求之间提交不同值的并发写事务,它保证每次从数据库读取时都获得相同的值。
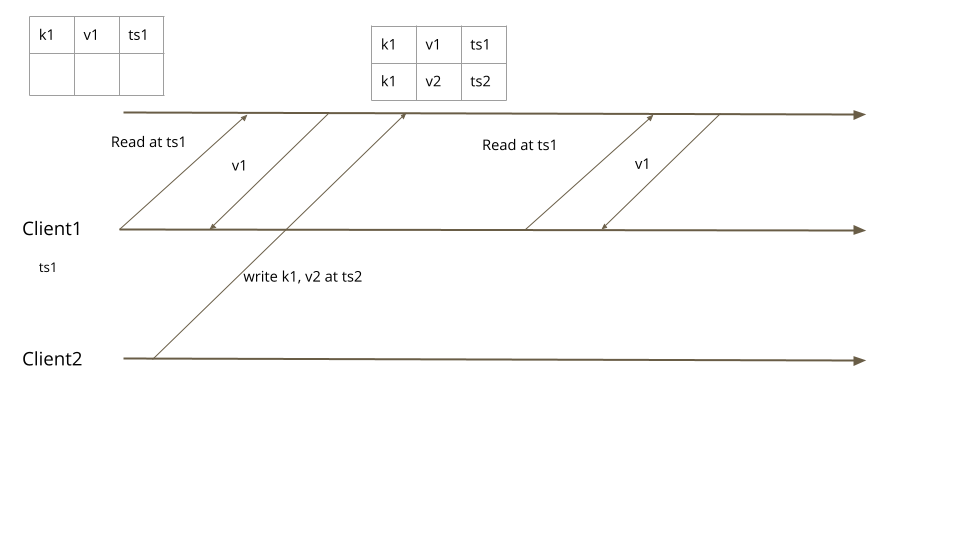
快照读
使用像 RocksDb 存储引擎
使用 rocksdb 或类似的嵌入式存储引擎作为数据存储的存储后端是非常常见的。例如,etcd 使用 boltdb, cockroachdb 更早使用 rocksdb,现在使用的是 rocksdb的 go-lang 版本的克隆产品 pebble。
这些存储引擎提供了适合存储 versioned 值的实现。与上一节描述的相同它们内部使用跳表的方式,并依赖于键的顺序。也可以提供自定义比较器为键排序。
class VersionedKeyComparator…
public class VersionedKeyComparator extends Comparator {
public VersionedKeyComparator() {
super(new ComparatorOptions());
}
@Override
public String name() {
return "VersionedKeyComparator";
}
@Override
public int compare(Slice s1, Slice s2) {
VersionedKey key1 = VersionedKey.deserialize(ByteBuffer.wrap(s1.data()));
VersionedKey key2 = VersionedKey.deserialize(ByteBuffer.wrap(s2.data()));
return key1.compareTo(key2);
}
}
使用 rocksdb 可以实现如下操作:
class RocksDBMvccStore…
private final RocksDB db;
public RocksDBMvccStore(File cacheDir) throws RocksDBException {
Options options = new Options();
options.setKeepLogFileNum(30);
options.setCreateIfMissing(true);
options.setLogFileTimeToRoll(TimeUnit.DAYS.toSeconds(1));
options.setComparator(new VersionedKeyComparator());
db = RocksDB.open(options, cacheDir.getPath());
}
public void put(String key, int version, String value) throws RocksDBException {
VersionedKey versionKey = new VersionedKey(key, version);
db.put(versionKey.serialize(), value.getBytes());
}
public String get(String key, int readAtVersion) {
RocksIterator rocksIterator = db.newIterator();
rocksIterator.seekForPrev(new VersionedKey(key, readAtVersion).serialize());
byte[] valueBytes = rocksIterator.value();
return new String(valueBytes);
}
例子
etcd3 背后使用 MVCC 与一个单一的整数表示一个版本。
mongodb和 cockroachdb 背后使用 MVCC 混合逻辑时钟。